WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY?

Introduction
Blockchain technology, often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is a revolutionary innovation with far-reaching implications beyond digital currencies. It is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures security, transparency, and immutability. This article will explore what blockchain technology is, how it works, its key features, applications, benefits, and challenges. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why blockchain is considered one of the most transformative technologies of our time.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Definition and Basic Concepts
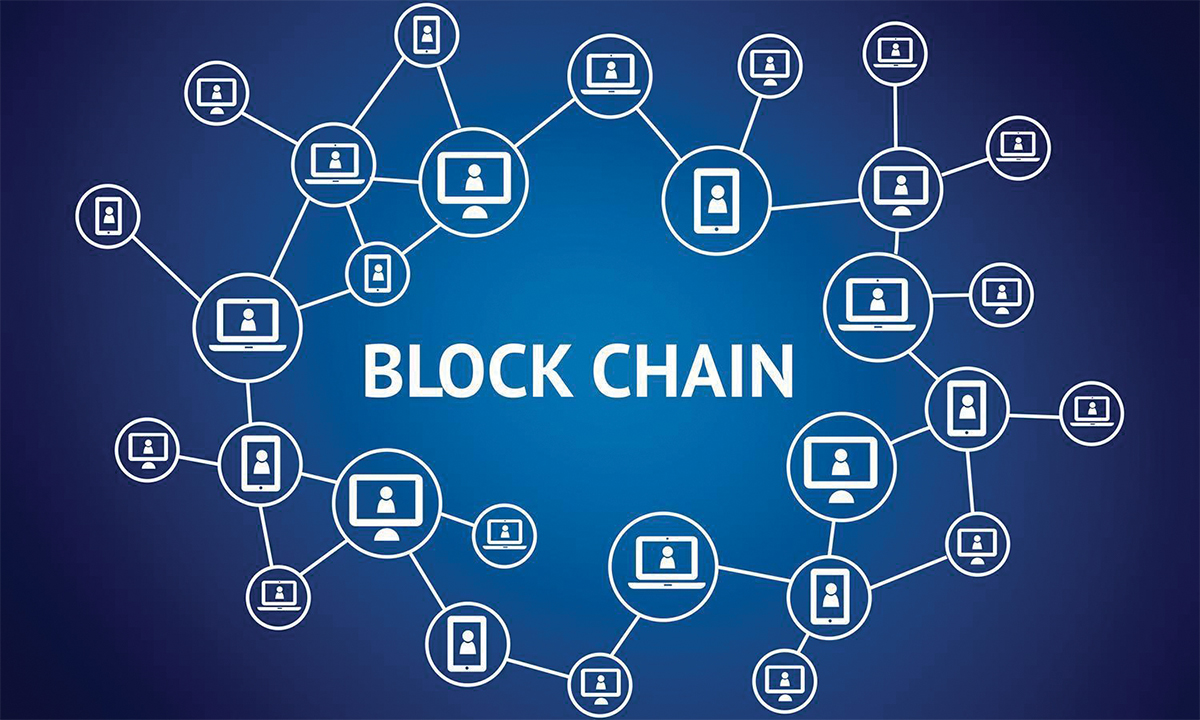
At its core, blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain. Each block in the chain contains multiple transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger.
Key Components of Blockchain
- Blocks: Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block.
- Chain: The chain is a sequence of blocks linked together in chronological order.
- Nodes: Nodes are computers that participate in the blockchain network, maintaining copies of the blockchain and validating transactions.
- Consensus Mechanism: A protocol used by the network to agree on the validity of transactions. Common mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
How Blockchain Works
- Transaction Initiation: A user requests a transaction, which is then broadcast to the network.
- Validation: Nodes in the network validate the transaction based on a consensus mechanism.
- Block Creation: Once validated, the transaction is included in a block along with other transactions.
- Linking Blocks: The new block is added to the blockchain, linked to the previous block by a cryptographic hash.
- Confirmation: The transaction is confirmed and recorded across all copies of the blockchain, making it immutable and transparent.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority. This decentralization enhances security and reduces the risk of single points of failure.
Transparency
All transactions on a blockchain are recorded on a public ledger, making the data transparent and accessible to all participants. This transparency fosters trust among users.
Immutability
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity and reliability of the data.
Security
Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. The use of hashes and digital signatures protects against fraud and unauthorized access.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute transactions when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain ensures secure and transparent transactions, underpinning the operation of these digital currencies.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and traceability. By recording every transaction, from production to delivery, blockchain helps track the origin and movement of goods, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
Healthcare
Blockchain can secure patient data, improve data interoperability, and streamline administrative processes. It allows for secure sharing of medical records between providers while maintaining patient privacy.
Finance
In the financial sector, blockchain facilitates faster and cheaper cross-border payments, improves the efficiency of financial processes, and enhances security. It is used in applications ranging from remittances to trade finance.
Real Estate
Blockchain can simplify real estate transactions by providing a secure and transparent platform for property records, reducing fraud and speeding up the process of buying and selling property.
Voting
Blockchain-based voting systems can enhance the security, transparency, and integrity of elections. By providing a tamper-proof record of votes, blockchain can help prevent electoral fraud and ensure accurate results.
Digital Identity
Blockchain can provide a secure and verifiable digital identity solution, reducing identity theft and fraud. Users can control their personal information and share it with trusted parties.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Blockchain can enhance the security and reliability of IoT networks by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger for recording device interactions and transactions.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Enhanced Security
The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchain provides high levels of security, protecting data from tampering and unauthorized access.
Improved Transparency
Blockchain’s transparency allows all participants to see the same data, fostering trust and accountability.
Increased Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes with smart contracts, blockchain can streamline operations and reduce transaction times and costs.
Auditability
Blockchain provides an immutable record of transactions, making it easy to audit and verify the authenticity of data and transactions.
User Control
Users have control over their data and transactions, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and intermediaries.
Challenges and Limitations
Scalability
Blockchain networks can face scalability issues, as the process of validating and recording transactions can be slow and resource-intensive, especially with a large number of users.
Regulation
The regulatory environment for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving, with different countries adopting varying approaches. This uncertainty can hinder adoption and innovation.
Energy Consumption
Blockchain networks that use Proof of Work, such as Bitcoin, consume significant amounts of energy, raising environmental concerns.
Interoperability
Different blockchain networks often operate in isolation, and achieving interoperability between them can be challenging.
Complexity
The technical complexity of blockchain technology can be a barrier to entry for individuals and organizations without the necessary expertise.
Future Prospects of Blockchain Technology
Adoption and Integration
As understanding and acceptance of blockchain grow, its adoption across various sectors is expected to increase. Governments, businesses, and institutions are exploring ways to integrate blockchain into their operations to enhance efficiency and security.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in blockchain technology, such as the development of more scalable and energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, will address current limitations and expand its potential applications.
Regulatory Clarity
The establishment of clear regulatory frameworks will provide certainty and encourage investment and innovation in blockchain technology.
Increased Interoperability
Efforts to improve interoperability between different blockchain networks will enhance the functionality and usability of blockchain-based solutions.
Mainstream Applications
Blockchain is likely to become a mainstream technology, underpinning a wide range of applications from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and digital identity.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to transform various industries and reshape the global economy. Its features of decentralization, transparency, immutability, and security provide significant advantages over traditional systems. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and increasing adoption indicate a promising future for blockchain. Understanding this technology and its implications is essential as we move towards a more connected and decentralized world.